The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a leader in the adoption of super apps, with nearly 1.4 billion mobile wallet users, accounting for half of the global total. By 2025, the usage of mobile wallets is expected to reach 4.9 billion globally (Source: Statista). This growth in digital financial services presents banks with a unique opportunity to expand their reach, increase customer engagement, and drive financial inclusion.
With high mobile internet penetration expected to reach 61% by 2030 (Source: Statista) and a young, digitally savvy population, APAC region has become a leading market for super apps. These platforms integrate a range of services including banking, payments, e-commerce, and transportation into one mobile app. For banks super apps are vital to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
In our previous blog, we explored how super apps and super wallets are the next step in the Middle East, driven by increasing smartphone adoption of smartphones and growing demand for mobile-first solutions. Now, as we shift focus to the Asia-Pacific region, the adoption of super apps is transforming the financial landscape, providing banks with new opportunities to innovate.
Types of e-Wallets
E-wallets play a crucial role in modernizing financial services by providing convenient and flexible payment solutions. Here’s a closer look at the three main types of e-wallets, each tailored to meet diverse customer needs and expectations.
- Pass-Through Wallet: Stores tokenized card information without holding funds. When a customer initiates a payment, the token is sent to the acquirer and then to the card scheme for verification with the card issuer. Only the card scheme and issuer are aware of the account details, ensuring a high level of security. Examples of pass-through wallets include Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay.
- Staged Wallet: Completes transactions in two stages. First, funds are transferred from various sources such as a bank account or card into the wallet. Then, in the second stage, the payment is sent to the merchant. This approach keeps payment details secure and encrypted. Examples of staged wallets include PayPal and Cash App.
- Stored Wallet: Holds a prepaid balance within the wallet, allowing customers to add funds from various sources such as bank accounts or cards. Customers can make direct payments from the wallet balance without needing to link their bank account or card details for every transaction. Examples of stored wallets include Alipay and WeChat Pay.
Why e-Wallets have Become the Dominant Payment Method in the APAC Region
Today, consumers value convenience above all. As digital transactions continue to increase in the APAC region, customers used digital wallets for 70% of e-com transaction value and 50% of POS spend in 2023. This growing demand for integrated services makes super apps essential in meeting the needs of APAC’s digitally savvy population, merging banking with lifestyle and daily activities to create a unified experience.
But why have digital wallets become the dominant payment methods in the APAC and why do they continue to thrive? One of the key reasons behind the success is their ability to seamlessly incorporate loyalty programs into the payments process, gamifying the experience and making it an attractive option for end-users. This integration enhances customer engagement and improves customer loyalty, as customers are rewarded for their spending habits.
The rise of cryptocurrencies has further strengthened digital wallets in the APAC region. As more merchants and SMEs begin to access cryptocurrencies, digital wallets have evolved to support these transactions, offering customers diverse and modern payment solutions. This adaptability ensures that digital wallets remain at the forefront of payment technology, catering to the evolving preferences of tech-savvy consumers.
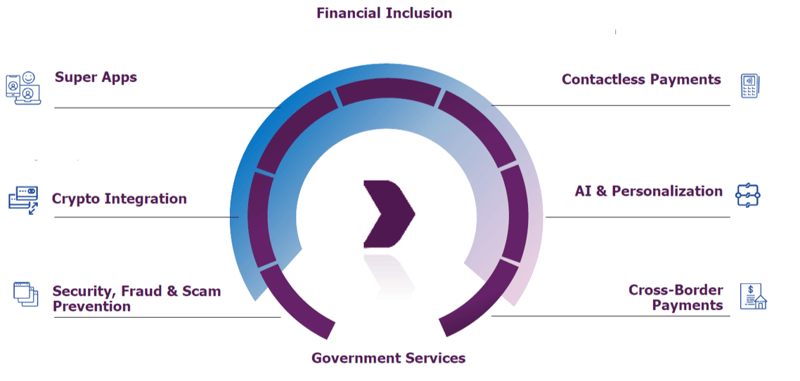
Regulatory support has also been instrumental in the widespread adoption of digital wallets across APAC. Governments have implemented strong regulations that promote the use of digital payments while ensuring security, making them a preferred payment method. In addition, advancements such as contactless payments, AI drive personalization, and fraud detection cater to the needs of a digitally savvy population, providing a convenient, secure, and rewarding payment experience.
E-Wallet Spheres of Application
Super apps enable banks to integrate themselves directly into customers’ daily lives by offering access to a range of financial and non-financial services on a single platform. For example, customers can make bill payments, shop online, book transportation, order food or groceries, access microloans, insurance products and saving accounts. This continuous engagement builds loyalty, as customers can perform multiple activities, from payments to shopping, without needing to switch apps. Banks can also leverage the data from these interactions to offer tailored financial products, improving customer satisfaction and retention.
While APAC’s high rate of digital adoption, more than 1 billion people in the region remain unbanked or underbanked.
Download our report to explore Digital Banking in Asia-Pacific.

Distribution of Adult Population
Despite a growing GDP and middle class, achieving widespread financial inclusion still represents a significant hurdle for the Asia Pacific region. In fact, driven by a limited amount of ATMs, Points of Sale (POS), few brick-and-mortar banks in rural areas and a generally cash driven culture, it is estimated that over 1 billion people in the region do not have access to formal financial services. Specifically, nearly 75% of the population in South-East Asia is either underbanked or completely unbanked.
Super apps provide a solution to reach these populations, offering accessible financial services. Banks can expand their reach, promote financial inclusion, and support underserved communities in areas with limited access to physical banking infrastructure, especially in regions with high smartphone penetration. They enable users to access essential financial services and support local economies through microloans and digital payments.
Benefits of Super Apps for Customers:
-
Efficiency: Super apps simplify daily tasks such as bill payments, online shopping, booking transportation, making daily activities easier and saves time.
Examples of Successful Super Apps in APAC
According to research, digital wallets have a 73% share of e-commerce payments in Asia, compared to just 15% for cards. This shift highlights the growing convenience in daily transactions for consumers across the region (Source: Asia-Pacific payments market trends - PCMI).
The APAC region has some of the most successful super apps transforming the digital landscape by offering a comprehensive range of services beyond their original scope. Grab, originally a ride-hailing service, has evolved into a comprehensive platform that now includes payments, food delivery, and hotel booking. In China, WeChat has set the benchmark for super apps. Initially a messaging app, WeChat has expanded to include payments, e-commerce, bill payments, and even appointment booking, all integrated within one platform. Alipay, another super app, has transformed digital payments and financial services in China and beyond, offering wealth management, insurance, online shopping, and travel bookings, creating a holistic ecosystem for users. Other examples include Paytm in India, Kakao Pay in South Korea, Momo in Vietnam, Touch ‘N’ Go in Malaysia and Gojek in Indonesia.
Super apps are transforming the financial landscape in APAC. For banks, these platforms offer an invaluable opportunity to reach new customers, drive financial inclusion, and build meaningful partnerships. As APAC’s digital economy continues to grow, super apps are likely to remain central to the future of banking, providing a dynamic channel for banks to engage digital-first consumers.
As the region continues to lead in mobile innovation, super apps will not only shape the future of banking in APAC but could also serve as a model for financial transformation worldwide.






